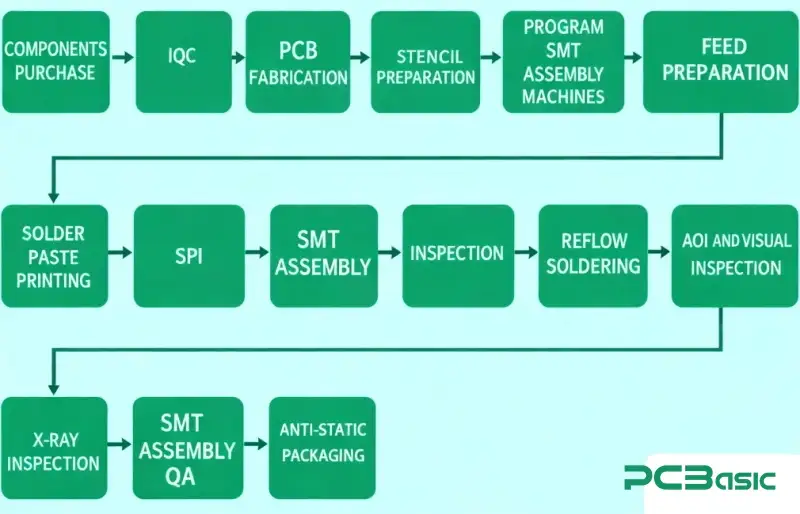
Designing an efficient Montageprozess is critical for any manufacturing operation aiming to reduce costs, improve quality, and increase throughput. A well-structured assembly process impacts everything from raw material utilization to finished product delivery, directly influencing customer satisfaction and a company’s competitive edge. In today’s dynamic global market, where consumer demands are constantly evolving and supply chains face unprecedented challenges, the ability to rapidly adapt and execute a lean Montageprozess is no longer just an advantage—it’s a necessity for survival and growth. This article delves into the core principles and practical steps involved in creating an assembly line that operates at peak efficiency, setting a benchmark for operational excellence.

Overview
- An efficient Montageprozess is fundamental for cost reduction, quality improvement, and increased production throughput.
- Careful planning and standardization are the initial steps to streamline any assembly operation.
- Integrating advanced technologies like robotics and data analytics can significantly boost efficiency and precision.
- Adopting lean manufacturing principles helps identify and eliminate waste within the Montageprozess.
- Continuous feedback loops and regular audits are essential for ongoing optimization and problem-solving.
- A well-trained and ergonomically supported workforce is vital for consistent quality and productivity.
- Evaluating layout, material flow, and cycle times are key components of process design.
Grundlagen eines Effizienten Montageprozesses (Foundations of an Efficient Assembly Process)
The journey to an efficient Montageprozess begins with a robust foundational understanding and meticulous planning. Before any physical changes are made, a thorough assessment of the current state is essential. This involves mapping out every step, identifying bottlenecks, and quantifying wasted time or resources. Key considerations include product design for manufacturability (DFM), which ensures that components are easy to assemble, reducing complexity and potential errors. Standardization plays a pivotal role; by standardizing parts, tools, and procedures, variability is minimized, leading to more predictable outcomes and easier training for new personnel.
The physical layout of the assembly line profoundly impacts efficiency. A linear flow, minimizing unnecessary movement of parts and personnel, is often ideal. Concepts like cellular manufacturing, where related tasks are grouped, can also significantly reduce transit times and inventory. Furthermore, understanding cycle times for each task and balancing the workload across workstations prevents bottlenecks and ensures a smooth, continuous flow. This initial phase requires detailed data collection, process mapping, and a commitment to understanding every nuance of the existing or proposed Montageprozess. In many regions, including the US, manufacturers are investing heavily in this foundational analysis to gain a competitive edge.
Technologieintegration im Modernen Montageprozess (Technology Integration in the Modern Assembly Process)
Modern technology offers powerful tools for optimizing the Montageprozess. Automation and robotics are no longer futuristic concepts but practical applications that can drastically improve speed, precision, and safety. Collaborative robots (cobots), for instance, can work alongside human operators, handling repetitive or physically demanding tasks, thereby freeing up human workers for more complex, cognitive functions. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) or autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) can manage material transport, ensuring parts arrive precisely when and where they are needed, reducing manual labor and potential for human error.
Beyond physical automation, data analytics and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) are revolutionizing how assembly lines operate. Sensors can monitor machine performance, product quality, and even environmental conditions in real-time. This data can then be analyzed to predict maintenance needs, identify quality deviations, and pinpoint inefficiencies in the Montageprozess almost instantaneously. Predictive maintenance, powered by AI, helps avoid costly downtime, while real-time feedback loops allow for immediate adjustments to production parameters. Implementing these technologies requires careful planning, robust cybersecurity measures, and a phased approach to integrate new systems seamlessly with existing infrastructure.
Prozessoptimierung und Kontinuierliche Verbesserung im Montageprozess (Process Optimization and Continuous Improvement in the Assembly Process)
An efficient Montageprozess is not a static achievement but an ongoing pursuit of perfection. Lean manufacturing principles are central to this continuous improvement. These principles focus on identifying and eliminating the seven wastes: overproduction, waiting, unnecessary transport, over-processing, excess inventory, unnecessary motion, and defects. Techniques like Value Stream Mapping (VSM) help visualize the entire process, highlighting areas where waste can be reduced. Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory management ensures that materials are procured and supplied only when needed, minimizing storage costs and reducing the risk of obsolescence.
The implementation of robust quality control measures is another critical aspect of process optimization. This includes methods like Poka-Yoke (mistake-proofing) to prevent errors from occurring and statistical process control (SPC) to monitor and control the production process. Regular audits and performance reviews provide opportunities to assess the effectiveness of current methods and identify new areas for improvement. A culture of continuous improvement, often supported by methodologies like Six Sigma or Kaizen, encourages all employees to actively seek out and implement small, incremental changes that collectively lead to significant gains in the Montageprozess over time.
Personal und Training für einen Robusten Montageprozess (Personnel and Training for a Robust Assembly Process)
Even with the most advanced technology and meticulously designed layouts, the human element remains indispensable to a successful Montageprozess. A skilled, well-trained, and motivated workforce is paramount. Comprehensive training programs are essential, not just for new hires but also for existing employees to keep them updated on new technologies, procedures, and quality standards. This training should cover both technical skills and soft skills, such as problem-solving and teamwork, as these are crucial for dynamic manufacturing environments.
Ergonomics plays a significant role in both efficiency and employee well-being. Designing workstations that minimize strain, reduce repetitive movements, and provide comfortable working conditions can prevent injuries, reduce absenteeism, and improve overall productivity. Investing in ergonomic tools and adjustable workstations pays dividends in long-term employee health and retention. Creating a safe and empowering work environment where employees feel valued and their input is respected fosters a sense of ownership and encourages proactive participation in process improvement. Ultimately, a strong focus on people, alongside process and technology, solidifies the foundations of an efficient and resilient Montageprozess.